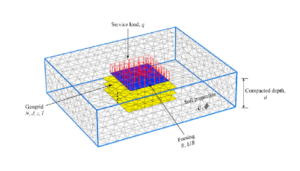
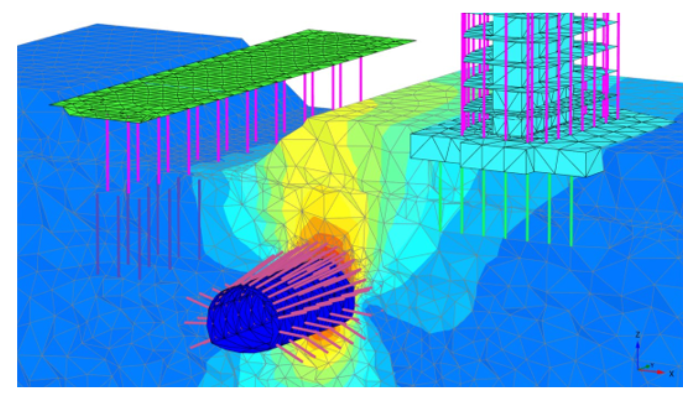
Introduction: Plaxis Software
Plaxis Software is a Finite Element Software tool designed for geotechnical engineering/geology for the analysis of deformation, stability, and groundwater flow in soil and rock. The first version of Plaxis software was launched in 1980 and developed by a team of researchers at Delft University of Technology in the Netherlands.
The purpose of this software is to solve the problems related to deformation Analysis, Stability Analysis, Groundwater Flow, and Soil-Structure Interaction.
Plaxis Software Is Used By,
Here are some of the groups the companies, or organizations that use Plaxis software,
- Geotechnical Students– Geotechnical Engineering Students from Mtech, PhDs, use the PLAXIS software for their learning and project work about soil, rock mechanics, soil behavior, slope stability, new materials, and foundation-level construction techniques.
- Professional– Civil Engineering Professionals working on PLAXIS software for foundation design, earthwork analysis, Tunneling, and landfill design works. Geologists also use it for assessing slope stability and Analyzing landslide risk.
- Geotechnical Consultancies – To improve project efficiency and enhance design confidence, companies work on the Foundational design, Slope Stability Analysis, and Earthquake Design in the PLAXIS 2D and 3D Software
Advantages Of Plaxis Software:
Plaxis Software has many advantages:
- Complex Numerical Techniques:
The first advantage of Plaxis software is to perform complex numerical techniques it uses finite element modeling (FEM) to provide precise and comprehensive simulations.
- Adaptable Constitutive Frameworks:
The second advantage is that it adapts the constitution framework by allowing for real behavior of materials simulation with a range of soil and rock models, including Mohr-Coulomb, Hardening Soil, and Jointed Rock.
- 2D and 3D Functions:
2D and 3D dimension functions play a vital role in the Geotechnical Simulations. Plaxis 2D can manage the Flat pressure and axisymmetric issues, and complex three-dimensional analyses issue handled by Plaxis 3D.
- Dynamic Simulation:
In the PLAXIS Software, you can perform a dynamic simulation for such movements, earthquakes, and other phenomena that change over time.
- Flooding and Stability:
Lastly, flooding and stability mean studies of the leakage of groundwater and its dependence on time reorganization, which is vital to understanding how soil behaves in various environments.
Key Features of Plaxis Software:
FEM Modeling
Plaxis software is used for advanced FEM to current analyze difficult geotechnical issues. 2D and 3D modeling Designs developed in the PLAXIS software can also help you perform simulations for the most advanced and complex modeling designs.
It contains several foundation models, including the Mohr-Coulomb, Jointed Rock, Hardening Soil, and Soft Soil models. It allows users to enter and modify the features of rock and soil to match certain project requirements.
Analysis Tools:
In Plaxis software, you can get the advanced features of analytics like
- Static Analytics is used to help determine how structures could respond to rigid loads,
- Dynamic analytics helps to study the impacts of changing loads like vibrations and seismic activity,
- Consolidation Analysis helps to show how soils behave in terms of time-dependent settlement when under load.
- Thermo-Hydro-Mechanical (THM) Analysis study considers mechanical, hydrological, and thermal characteristics.
2D and 3D Simulation:
To analyze the perfect axisymmetric situation and straight-line strain problems commonly used by Plaxis 2D. To solve a complex geotechnical-related issue by PLAXIS 3D.
Seepage and Groundwater Flow:
You can analyze and review water flow through soil, which is important to know about the effects of groundwater through Seepage Analysis, and also analyze how the physical surface affects soil stability with the help of Physical Surface Modeling features.
Simple Graphical User Interface (GUI):
Plaxis software offers the features of the user interface, visuals, and design:
- Improve the process of creating models, putting boundary conditions on them, and visualizing the outcomes,
- Making it easier to sketch complex structures and geometries and
- Offers powerful visualization tools, such as stress distributions, displacement vectors, and contour plots.
Applications of Plaxis Software:
Plaxis Software is used in geotechnical engineering for different applications use Here are some applications:
- Foundation Analysis:
In structure analysis, there are 2 types of structure. Shallow structure Analysis of the weight and movement of tiles and other weak foundations, and deep structure measures how well the deep footing of piles and bridges is under different types of loading.
- Slope Stability Analysis:
PLAXIS software helps to check the safety and stability of natural slopes to prevent disasters like landslides. Also, check the perforation of walls, dams, and earth structures.
PLAXIS also analyzes the soil strength variations and seismic loading when analyzing slope stability.
- Tunnels Design:
The software performs the Tunnel modeling and simulations facility to check the strength of the structure, load distribution, stability of the tunnel, and earth movement by modeling the tunnel building and maintainable phases, and also analyzes other underground construction.
How to use Plaxis Software:
To use Plaxis Software, there are numerous steps that you have to follow. Here are the steps:
1. Set Up Project:
Be clear about your goal, its limitations, and the expected result of the geotechnical problem, then collect all the information required, including soil characteristics, geometry, loading circumstances, groundwater conditions, and specifics of the construction process.
2. Establish the Geometry for the Modeling:
To set up the problem geometry, use geometry generation tools. Choose the software type of 2D or 3D as per your requirements. Make a 2D cross-section for Plaxis 2D. Make a full 3D model for Plaxis 3D. After that, you define the boundary to represent a geotechnical issue correctly.
3. Meshing:
There are 2 types of meshes: General Mesh and Refined Mesh:
- General Mesh – To divide the geometry into individual elements and crested FEM model. Use Fine mesh in important areas where higher precision is required.
- Refined Mesh is used in important areas like retaining walls, tunnels, and foundations. The mesh is a smaller element in areas with more accuracy that is used in complex modeling work.
PLAXIS software also allows you to quality-check the mesh that you applied for the modeling. Ensure that elements have been properly applied to the mesh as per the standard ratio.
4. Give Material Qualities:
- Choose a relevant structure model for soil and rock from the Plaxis library like Mohr-Coulomb, Hardening Soil Model, and Soft Soil Creep.
- After that, enter the important material quality, like density, cohesion, friction angle, modulus of elasticity, and permeability, for each layer or zone of soil and rock
5. Explain Border Issues and Loading:
- Border Issues are used for issues related to physical limits, like fixing roller boundaries, and issues-free no movement.
- Describe the many kinds of loads, such as dynamic loads (such as earthquakes) and static loads (such as buildings and traffic). Indicate the size, orientation, and length of these loads.
6. Calculations:
After applying the meshing work on the modeling, you can start running a calculation process, PLAXIS software runs calculations based on any of the complex modeling simulations. You can monitor the progress on the display of the software and see if any errors are encountered during the calculation process.
7. Post-Processing and Result Analysis:
After completion of the calculation process, PLAXIS offers results in a different format of tables and graphs in visualizations. That covers the different values of the loads, displacements, pressure, etc.
8. Understand The Result:
In these steps, you can analyze your results, like visual results, analyze data, and generate the report.
- For Visual results, you can use the post-processing tool of Plaxis,
- Under analyzing data, you analyze how the soil structure behaves under load and identify weak areas of failure.
- Last, you generate a reported joint analysis result in reports like graphical outputs and detailed data tables.
Plaxis Software Training Courses:
There are multiple courses and training programs available on the internet that you can enroll in and gain the expertise of the Plaxis software. In this category, there is one of the professional certification training programs that we offer, hands-on training on the software and project assistance support, also by the industry professionals who have spent years in this software to deal with Geotechnical Engineering Projects.
PIGSO LEARNING offered a live certification training program on the PLAXIS software training now. You can get more information from the website and download the syllabus.
Types Of Plaxis Software:
There are 2 types of Plaxis software, PLAXIS 2D and 3D help to analyze different geotechnical engineering problems.
Plaxis 2D software
Plaxsi 2D is a finite element software. It is specially designed for any movement and stability in 2D (two dimensions) in geotechnical engineering. It is used in modeling soil and rock behavior under various loading conditions, and soil-structure interactions in a plane strain or axisymmetric context.
Plaxis 3D software
Plxis 3D is a finite element software, it is designed for analyzing 3D in geotechnical engineering. It manages complex 3D(three dimensions) problems, and it offers advanced features of 2D, which provide deep pictures with more details in geotechnical problems.
Different Between Plaxis 2D & Plaxis 3D Software:
Here are the key differences between Plaxis 2D and Plaxis 3D:
Dimensionality:
- Plaxis 2D: Plaxis 2D is specially designed for 2D or two-dimensional analysis. It solves the problem of geotechnical and loading issues such as plane strain or axisymmetric problems.
- Plaxis 3D: In Plaxis 3D, the feature in 2D increases in 3D. It solves the highly complex problem of geotechnical and loading issues in 3D analysis.
Applications:
- Plaxis 2D: It is used in foundation design to analyze deep foundations, footings, and piles under various loading conditions, slope stability to analyze the stability of slopes, embankments, and retaining walls, tunnel to analyze the behavior of tunnels, shafts, and deep excavations, and ground improvement method for soil stabilization and reinforcement.
- Plaxis 3D: It requires an exact 3D description of the physical interaction between soil and structures, and checks deep tunnels and under constructions with complex geometry.
Meshing:
- Plaxis 2D: Provide a 2D Finite element mesh perfect for axisymmetric geometries and plane strain. It offers triangular and rectangular element types for 2D.
- Plaxis 3D: Provide a 3D Finite element mesh that properly shows complex geometries and soil structure. It offers hexahedral and hexagonal element types for 3D.
Analysis Types:
- Plaxis 2D: Use Static and dynamic analytics to predict how the structure will respond to imposed load and analyze the impact of dynamic loads like an earthquake.
- Plaxis 3D: It performs the status loading and dynamic analysis to represent the transient and steady-state behaviors in 3D. It also analyses thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) and thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical (THMC) coupled analyses.
User Interface:
- Plaxis 2D: It has a simple interface for setting up the model, applying boundary conditions, and visualizing the results that are unique to 2D issues.
- Plaxis 3D: It has the same user interface but it has extra tools for managing complex geometries and volumetric data, specifically designed for 3D modeling and analysis.
Conclusion:
Plaxis is a strong and adaptable geotechnical analysis tool that may be used to solve a variety of geotechnical engineering problems, from slope stability to base design, and more. Through the implementation of the thorough steps and best methods defined in this manual, users can effectively use Plaxis to attain highly accurate and reliable outcomes in their geotechnical engineering tasks. PIGSO LEARNING always works to offer a comprehensive training program for engineering students, research scholars, and professionals.

Mayank Panchal is the founder of PIGSO Learning. He has many years of experience in teaching, curriculum development, and instructional designer in civil engineering, Mathematics, and digital marketing space. His passion for conceptual and deep research-based learning helps to understand the subject in depth.